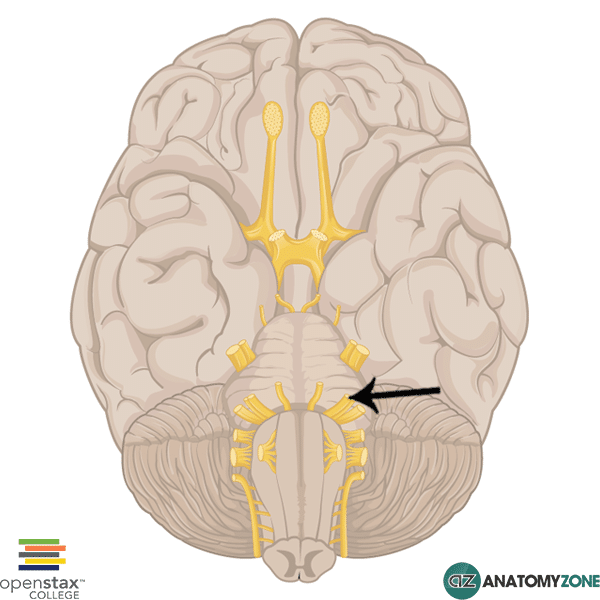
Facial Nerve
The structure indicated is the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII).
The facial nerve is responsible for supplying the muscles of facial expression. In addition, the facial nerve provides taste sensation to the anterior 2/3 of the tongue and secretomotor function to the salivary, lacrimal, nasal and palatine glands.
The facial nerve originates from the cerebellopontine angle, laterally at the junction between the pons and the medulla. It has two roots: a motor root and the nervus intermedius, which carries the parasympathetic and sensory fibres.
Intracranial branches
- Greater petrosal nerve
- Nerve to stapedius
- Chorda tympani
Extracranial branches
- Posterior auricular nerve
- Branches to stylohyoid and posterior belly of digastric
- 5 branches emerge from parotid gland: temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, cervical
The upper facial muscles receive bilateral innervation from upper motor neurones, whereas the lower facial muscles receive only contralateral innervation from the upper motor neurones. In a unilateral upper motor neurone lesion, the muscles to the forehead will therefore be spared due to the bilateral innervation. There is no sparing of the forehead muscles in a lower motor neuron lesion, resulting in complete ipsilateral weakness of the facial muscles.
Learn more about the cranial nerves in this anatomy tutorial.