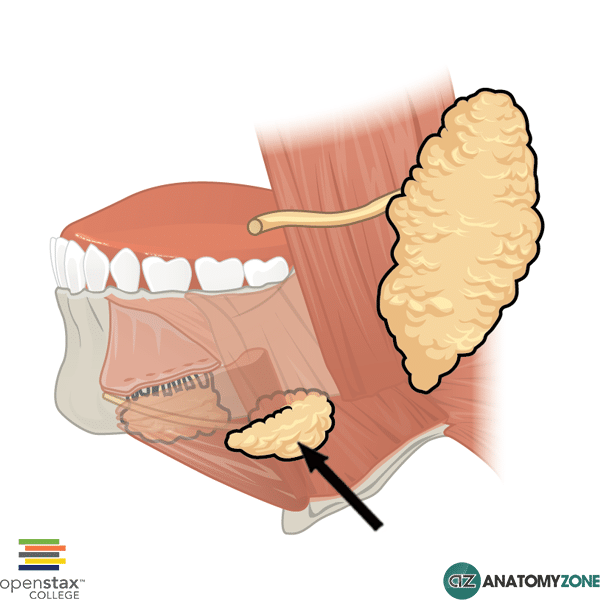
Submandibular Gland
The structure indicated is the submandibular gland.
There are three main large sets of salivary glands in the face:
- Parotid glands
- Submandibular glands
- Sublingual glands
The submandibular glands are hook shaped and consist of a deep part and a superficial part, separated by the mylohyoid muscle.
The deep part of the submandibular gland is formed from the shorter arm of the hook, which loops posteriorly around the mylohyoid muscle to enter the floor of the oral cavity.
The superficial part of the submandibular gland is formed from the longer arm of the hook and lies outside the oral cavity.
The duct of the submandibular gland (Wharton duct) opens adjacent to the inferior point of attachment of the frenulum.
The submandibular glands receive parasympathetic innervation via the chorda tympani branch of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII).