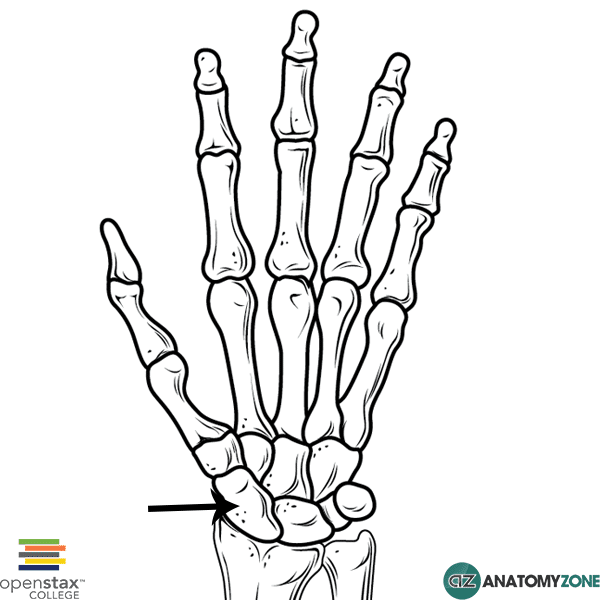
Scaphoid Bone
The structure indicated is the scaphoid bone.
There are three groups of bones in the hand:
- Carpal bones (8 in total)
- Metacarpal bones
- Phalanges
The carpal bones are separated into two rows:
- Proximal row
- Distal row
The scaphoid bone is one of four bones in the proximal row of carpals (scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform). The lunate bone is located centrally in the wrist between the scaphoid and triquetral bones. It gets its name from its crescent shape (lunar = relating to the moon). It has the following articulations:
- Proximal: Radius
- Distal: trapezoid and trapezium
- Medial: capitate and lunate
The scaphoid bone receives is vascular supply from the distal branches of the radial artery. The middle and distal portions of the bone are well supplied, but the proximal portion receives limited supply. This limited arterial supply to the proximal portion, is clinically significant in scaphoid fractures which are very common injuries following a fall on an outstretched hand and can result in avascular necrosis of the proximal segment, or other complications such as non-union/mal-union.
Learn more about the anatomy of the bones of the hand in this tutorial.