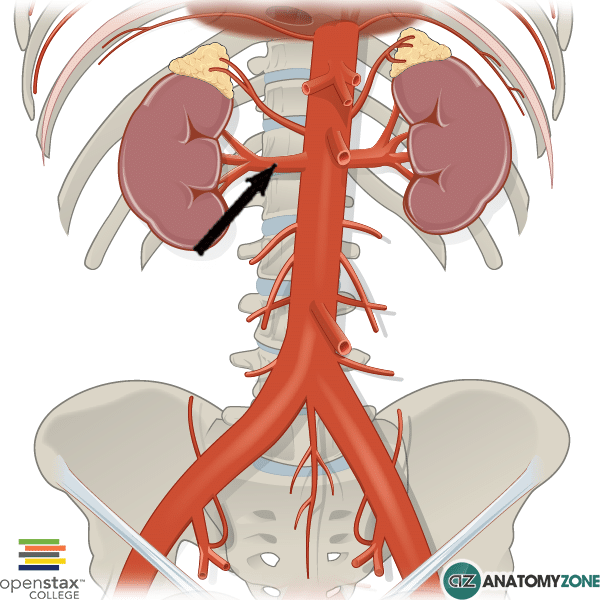
Renal Artery
The structure indicated is the right renal artery.
The renal arteries are lateral branches of the abdominal aorta which arise at the level of the intervertebral disc between L1 and L2, just below the origin of the superior mesenteric arteries. There is one renal artery that supplies each kidney. The right renal artery tends to originate slightly lower than the left renal artery, and it passes behind the inferior vena cava to supply the right kidney.
The renal arteries then divide into a few anterior and posterior branches at the hilum. The renal arteries can become narrowed, or stenosed (renal artery stenosis), which causes the perfusion to the kidney to lower, resulting in increased renin release which causes an increase in blood pressure via the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Learn more about the kidneys in this anatomy tutorial.