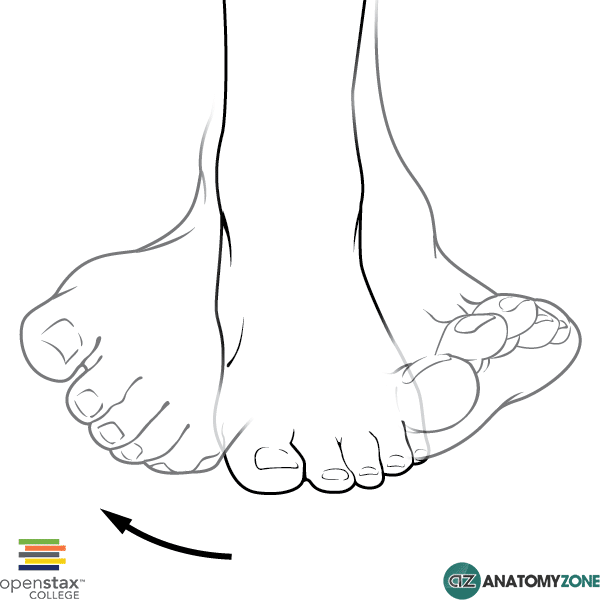
Inversion of the Foot
This diagram indicates inversion of the foot.
Inversion is a movement of the foot which causes the soles of the feet to face inwards, and eversion is the opposite movement.
Inversion and eversion occur primarily at:
- Talocalcaneonavicular joint
- Subtalar (talocalcaneal) joint
The muscles which cause inversion of the foot are:
- Tibialis anterior
- Tibialis posterior
The muscles which cause eversion of the foot are:
- Peroneus longus
- Peroneus brevis
Inversion injuries of the ankle are common, and result in ankle sprain affecting the ligaments on the lateral aspect of the ankle. Most commonly, the anterior talofibular ligament (70-85% of ankle sprains caused by forceful inversion) and the calcaneofibular ligament are torn. The posterior talofibular ligament can also be torn in ankle sprain.
To learn more about the anatomy of the ankle joint click here.