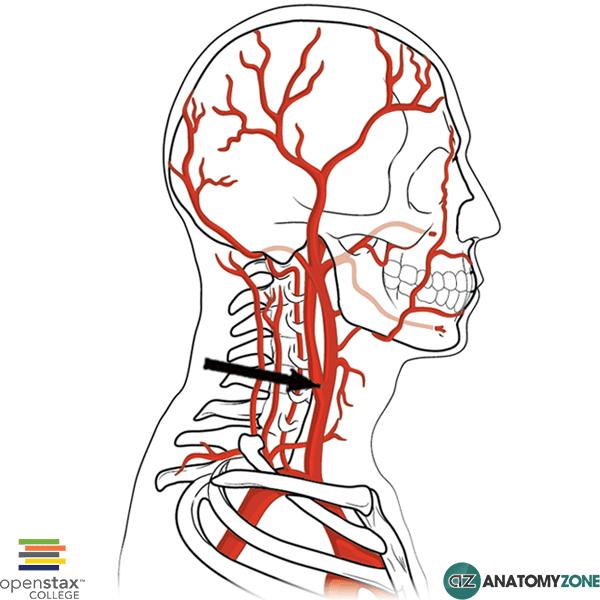
Carotid Sinus
The structure indicated is the carotid sinus.
The carotid sinus is located just above the bifurcation of the common carotid artery at the base of the internal carotid artery.
The carotid sinus is an important structure in regulating and maintaining blood pressure. It contains baroreceptors which are sensitive to increases in arterial blood pressure and subsequent increased pressure and stretching of the arterial walls. The carotid sinus receives innervation via cranial nerve IX (glossopharyngeal nerve). This nerve synapses in the nucleus tractus solitarii of the medulla oblongata which then indirectly adjusts the level of autonomic outflow and controls the body’s blood pressure by altering the cardiac output and smooth muscle tone in the vasculature.
Also located at the bifurcation of the common carotid artery are chemoreceptors which detect changes in the partial pressure of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood. This collection of chemoreceptors are known as the carotid body, and receives innervation via cranial nerves IX and X.