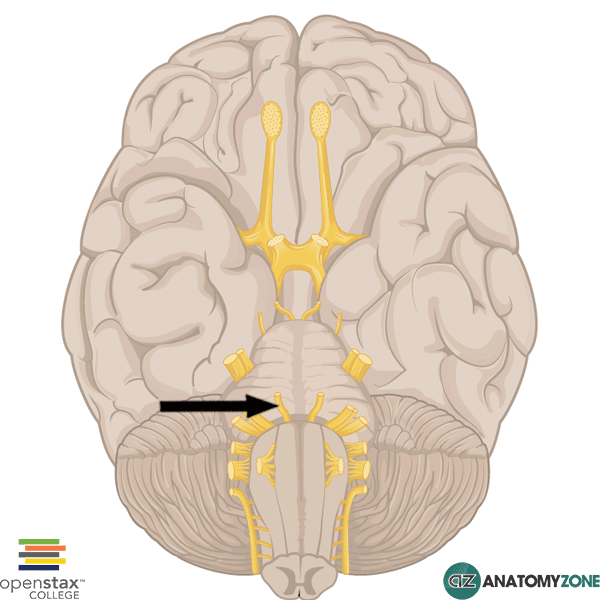
Abducent Nerve
The structure indicated is the abducent nerve (cranial nerve VI).
The abducent nerve (cranial nerve VI), provides general somatic efferent fibres (motor function) to the lateral rectus muscle of the eye. There are three cranial nerves which are responsible for innervating the extrinsic muscles of the eye:
- Oculomotor nerve (cranial nerve III)
- Trochlear nerve (cranial nerve VI)
- Abducent nerve
The oculomotor nerve supplies the superior, inferior and medial rectus muscles, as well as the inferior oblique muscle and the levator palpebrae superioris.
The trochlear nerve supplies the superior oblique muscle.
It originates between the pons and the medulla of the brain stem. It has a long intracranial course which makes it vulnerable to injury: fractures of the petrous part of the temporal bone, aneurysms of the internal carotid artery and mass lesions all put this nerve at risk. Lesions of the abducent nerve cause diplopia on lateral gaze, with inability to abduct the affected eye – the eye is pulled medially due to the unopposed action of the medial rectus muscle.
Learn more about the cranial nerves in this anatomy tutorial