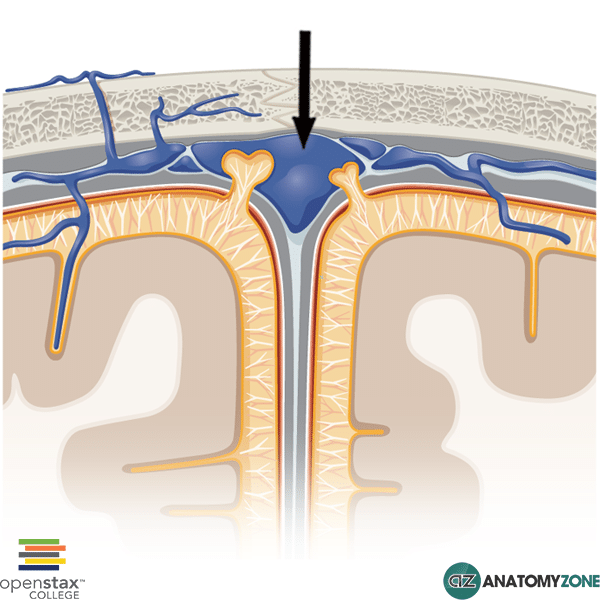
Superior Sagittal Sinus
The structure indicated is the superior sagittal sinus.
The brain is drained by a series of veins and venous channels which drain into large dural venous sinuses, which in turn ultimately drain to the internal jugular veins. The dural venous sinuses are lined by endothelium and located between the layers of the dura mater in the brain. The venous sinuses are different to other blood vessels as they do not have the same set of layers which form their walls, and do not contain valves, like veins.
The venous sinuses receive blood from veins which drain the brainstem, the cerebrum and the cerebellum, as well as diploic and emissary veins. Diploic veins run from inside the compact bone of the cranium into the venous sinuses, whereas emissary veins run from outside the cranium through the compact bone and into the venous sinuses.
The superior sagittal sinus is located on the superior border of the falx cerebri and receives blood from superior cerebral, diploic, and emissary veins, as well as receiving CSF via arachnoid granulations. It drains blood from lateral and anterior parts of the cerebrum into the confluence of sinuses.
The superior sagittal sinus beings at the foramen cecum and drains into the confluence of sinuses near the internal occipital protuberance.